How To Create Circular Linked List
We have discussed Singly and Circular Linked List in the following post:
Singly Linked List
Circular Linked List
Why Circular? In a singly linked list, for accessing any node of the linked list, we start traversing from the first node. If we are at any node in the middle of the list, then it is not possible to access nodes that precede the given node. This problem can be solved by slightly altering the structure of a singly linked list. In a singly linked list, the next part (pointer to next node) is NULL. If we utilize this link to point to the first node, then we can reach the preceding nodes. Refer to this for more advantages of circular linked lists.
The structure thus formed is a circular singly linked list and looks like this:
Attention reader! Don't stop learning now. Get hold of all the important DSA concepts with the DSA Self Paced Course at a student-friendly price and become industry ready. To complete your preparation from learning a language to DS Algo and many more, please refer Complete Interview Preparation Course .
In case you wish to attend live classes with experts, please refer DSA Live Classes for Working Professionals and Competitive Programming Live for Students.
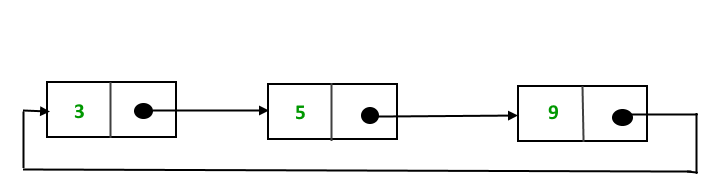
In this post, the implementation and insertion of a node in a Circular Linked List using a singly linked list are explained.
Implementation
To implement a circular singly linked list, we take an external pointer that points to the last node of the list. If we have a pointer last pointing to the last node, then last -> next will point to the first node.
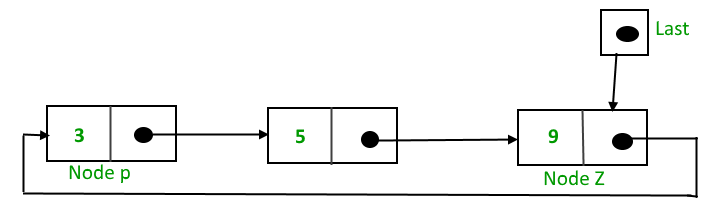
The pointer last points to node Z and last -> next points to node P.
Why have we taken a pointer that points to the last node instead of the first node?
For the insertion of a node at the beginning, we need to traverse the whole list. Also, for insertion at the end, the whole list has to be traversed. If instead of start pointer, we take a pointer to the last node, then in both cases there won't be any need to traverse the whole list. So insertion at the beginning or at the end takes constant time, irrespective of the length of the list.
Insertion
A node can be added in three ways:
- Insertion in an empty list
- Insertion at the beginning of the list
- Insertion at the end of the list
- Insertion in between the nodes
Insertion in an empty List
Initially, when the list is empty, the last pointer will be NULL.

After inserting node T,
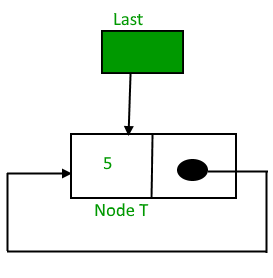
After insertion, T is the last node, so the pointer last points to node T. And Node T is the first and the last node, so T points to itself.
Function to insert a node into an empty list,
C++
struct Node *addToEmpty( struct Node *last, int data)
{
if (last != NULL)
return last;
struct Node *temp =
( struct Node*) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node));
temp -> data = data;
last = temp;
temp -> next = last;
return last;
}
Java
static Node addToEmpty(Node last, int data)
{
if (last != null )
return last;
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
last = temp;
temp.next = last;
return last;
}
Python3
def addToEmpty( self , data):
if ( self .last ! = None ):
return self .last
temp = Node(data)
self .last = temp
self .last. next = self .last
return self .last
C#
static Node addToEmpty(Node last, int data)
{
if (last != null )
return last;
Node temp =
new Node();
temp.data = data;
last = temp;
temp.next = last;
return last;
}
Javascript
<script>
function addToEmpty(last , data)
{
if (last != null )
return last;
var temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
last = temp;
temp.next = last;
return last;
}
</script>
Insertion at the beginning of the list
To insert a node at the beginning of the list, follow these steps:
1. Create a node, say T.
2. Make T -> next = last -> next.
3. last -> next = T.
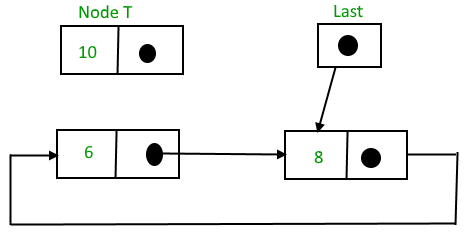
After insertion,
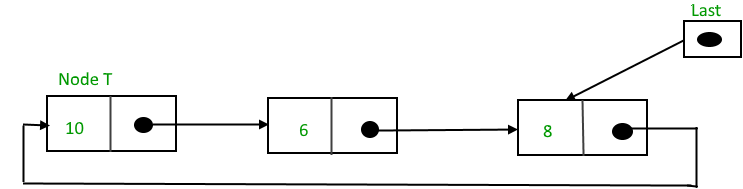
Function to insert nodes at the beginning of the list,
C++
struct Node *addBegin( struct Node *last, int data)
{
if (last == NULL)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
struct Node *temp
= ( struct Node *) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node));
temp -> data = data;
temp -> next = last -> next;
last -> next = temp;
return last;
}
Java
static Node addBegin(Node last, int data)
{
if (last == null )
return addToEmpty(last, data);
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
return last;
}
Python3
def addBegin( self , data):
if ( self .last = = None ):
return self .addToEmpty(data)
temp = Node(data)
temp. next = self .last. next
self .last. next = temp
return self .last
C#
static Node addBegin(Node last, int data)
{
if (last == null )
return addToEmpty(last, data);
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
return last;
}
Javascript
<script>
function addBegin(last , data)
{
if (last == null )
return addToEmpty(last, data);
var temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
return last;
}
</script>
Insertion at the end of the list
To insert a node at the end of the list, follow these steps:
1. Create a node, say T.
2. Make T -> next = last -> next;
3. last -> next = T.
4. last = T.
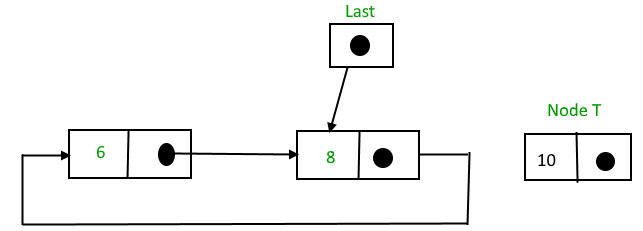
After insertion,
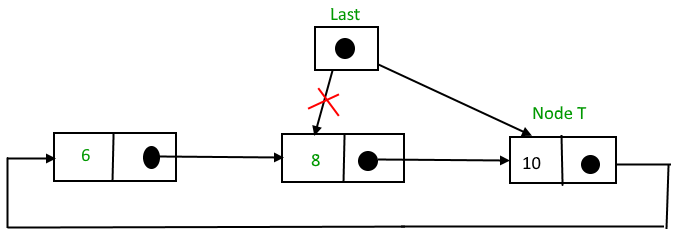
Function to insert a node at the end of the List
C++
struct Node *addEnd( struct Node *last, int data)
{
if (last == NULL)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
struct Node *temp =
( struct Node *) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node));
temp -> data = data;
temp -> next = last -> next;
last -> next = temp;
last = temp;
return last;
}
Java
static Node addEnd(Node last, int data)
{
if (last == null )
return addToEmpty(last, data);
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
last = temp;
return last;
}
Python3
def addEnd( self , data):
if ( self .last = = None ):
return self .addToEmpty(data)
temp = Node(data)
temp. next = self .last. next
self .last. next = temp
self .last = temp
return self .last
C#
static Node addEnd(Node last, int data)
{
if (last == null )
return addToEmpty(last, data);
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
last = temp;
return last;
}
Javascript
<script>
function addEnd(last, data) {
if (last == null ) return addToEmpty(last, data);
var temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
last = temp;
return last;
}
</script>
Insertion in between the nodes
To insert a node in between the two nodes, follow these steps:
1. Create a node, say T.
2. Search for the node after which T needs to be inserted, say that node is P.
3. Make T -> next = P -> next;
4. P -> next = T.
Suppose 12 needs to be inserted after the node has the value 10,
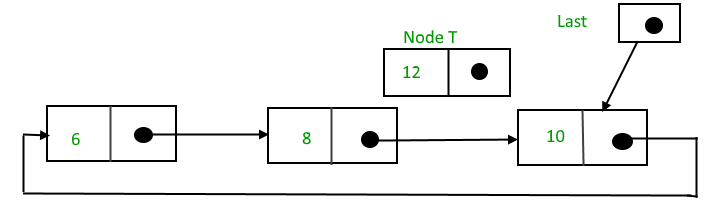
After searching and insertion,
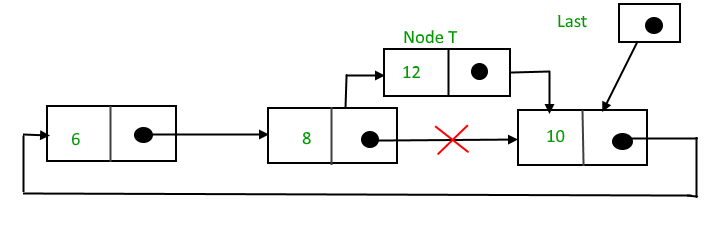
Function to insert a node at the end of the List,
C++
struct Node *addAfter( struct Node *last, int data, int item)
{
if (last == NULL)
return NULL;
struct Node *temp, *p;
p = last -> next;
do
{
if (p ->data == item)
{
temp = ( struct Node *) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node));
temp -> data = data;
temp -> next = p -> next;
p -> next = temp;
if (p == last)
last = temp;
return last;
}
p = p -> next;
} while (p != last -> next);
cout << item << " not present in the list." << endl;
return last;
}
Java
static Node addAfter(Node last, int data, int item)
{
if (last == null )
return null ;
Node temp, p;
p = last.next;
do
{
if (p.data == item)
{
temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = p.next;
p.next = temp;
if (p == last)
last = temp;
return last;
}
p = p.next;
} while (p != last.next);
System.out.println(item + " not present in the list." );
return last;
}
Python3
def addAfter( self , data, item):
if ( self .last = = None ):
return None
temp = Node(data)
p = self .last. next
while p:
if (p.data = = item):
temp. next = p. next
p. next = temp
if (p = = self .last):
self .last = temp
return self .last
else :
return self .last
p = p. next
if (p = = self .last. next ):
print (item, "not present in the list" )
break
C#
static Node addAfter(Node last, int data, int item)
{
if (last == null )
return null ;
Node temp, p;
p = last.next;
do
{
if (p.data == item)
{
temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = p.next;
p.next = temp;
if (p == last)
last = temp;
return last;
}
p = p.next;
} while (p != last.next);
Console.WriteLine(item + " not present in the list." );
return last;
}
Javascript
<script>
function addAfter(last, data, item) {
if (last == null ) return null ;
var temp, p;
p = last.next;
do {
if (p.data == item) {
temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = p.next;
p.next = temp;
if (p == last) last = temp;
return last;
}
p = p.next;
} while (p != last.next);
document.write(item + " not present in the list. <br>" );
return last;
}
</script>
The following is a complete program that uses all of the above methods to create a circular singly linked list.
C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
struct Node *addToEmpty( struct Node *last, int data)
{
if (last != NULL)
return last;
struct Node *temp =
( struct Node*) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node));
temp -> data = data;
last = temp;
last -> next = last;
return last;
}
struct Node *addBegin( struct Node *last, int data)
{
if (last == NULL)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
struct Node *temp =
( struct Node *) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node));
temp -> data = data;
temp -> next = last -> next;
last -> next = temp;
return last;
}
struct Node *addEnd( struct Node *last, int data)
{
if (last == NULL)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
struct Node *temp =
( struct Node *) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node));
temp -> data = data;
temp -> next = last -> next;
last -> next = temp;
last = temp;
return last;
}
struct Node *addAfter( struct Node *last, int data, int item)
{
if (last == NULL)
return NULL;
struct Node *temp, *p;
p = last -> next;
do
{
if (p ->data == item)
{
temp = ( struct Node *) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node));
temp -> data = data;
temp -> next = p -> next;
p -> next = temp;
if (p == last)
last = temp;
return last;
}
p = p -> next;
} while (p != last -> next);
cout << item << " not present in the list." << endl;
return last;
}
void traverse( struct Node *last)
{
struct Node *p;
if (last == NULL)
{
cout << "List is empty." << endl;
return ;
}
p = last -> next;
do
{
cout << p -> data << " " ;
p = p -> next;
}
while (p != last->next);
}
int main()
{
struct Node *last = NULL;
last = addToEmpty(last, 6);
last = addBegin(last, 4);
last = addBegin(last, 2);
last = addEnd(last, 8);
last = addEnd(last, 12);
last = addAfter(last, 10, 8);
traverse(last);
return 0;
}
Java
class GFG
{
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
};
static Node addToEmpty(Node last, int data)
{
if (last != null )
return last;
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
last = temp;
last.next = last;
return last;
}
static Node addBegin(Node last, int data)
{
if (last == null )
return addToEmpty(last, data);
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
return last;
}
static Node addEnd(Node last, int data)
{
if (last == null )
return addToEmpty(last, data);
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
last = temp;
return last;
}
static Node addAfter(Node last, int data, int item)
{
if (last == null )
return null ;
Node temp, p;
p = last.next;
do
{
if (p.data == item)
{
temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = p.next;
p.next = temp;
if (p == last)
last = temp;
return last;
}
p = p.next;
} while (p != last.next);
System.out.println(item + " not present in the list." );
return last;
}
static void traverse(Node last)
{
Node p;
if (last == null )
{
System.out.println( "List is empty." );
return ;
}
p = last.next;
do
{
System.out.print(p.data + " " );
p = p.next;
}
while (p != last.next);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node last = null ;
last = addToEmpty(last, 6 );
last = addBegin(last, 4 );
last = addBegin(last, 2 );
last = addEnd(last, 8 );
last = addEnd(last, 12 );
last = addAfter(last, 10 , 8 );
traverse(last);
}
}
Python3
class Node:
def __init__( self , data):
self .data = data
self . next = None
class CircularLinkedList:
def __init__( self ):
self .last = None
def addToEmpty( self , data):
if ( self .last ! = None ):
return self .last
temp = Node(data)
self .last = temp
self .last. next = self .last
return self .last
def addBegin( self , data):
if ( self .last = = None ):
return self .addToEmpty(data)
temp = Node(data)
temp. next = self .last. next
self .last. next = temp
return self .last
def addEnd( self , data):
if ( self .last = = None ):
return self .addToEmpty(data)
temp = Node(data)
temp. next = self .last. next
self .last. next = temp
self .last = temp
return self .last
def addAfter( self , data, item):
if ( self .last = = None ):
return None
temp = Node(data)
p = self .last. next
while p:
if (p.data = = item):
temp. next = p. next
p. next = temp
if (p = = self .last):
self .last = temp
return self .last
else :
return self .last
p = p. next
if (p = = self .last. next ):
print (item, "not present in the list" )
break
def traverse( self ):
if ( self .last = = None ):
print ( "List is empty" )
return
temp = self .last. next
while temp:
print (temp.data, end = " " )
temp = temp. next
if temp = = self .last. next :
break
if __name__ = = '__main__' :
llist = CircularLinkedList()
last = llist.addToEmpty( 6 )
last = llist.addBegin( 4 )
last = llist.addBegin( 2 )
last = llist.addEnd( 8 )
last = llist.addEnd( 12 )
last = llist.addAfter( 10 , 8 )
llist.traverse()
C#
using System;
public class GFG
{
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
};
static Node addToEmpty(Node last, int data)
{
if (last != null )
return last;
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
last = temp;
last.next = last;
return last;
}
static Node addBegin(Node last, int data)
{
if (last == null )
return addToEmpty(last, data);
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
return last;
}
static Node addEnd(Node last, int data)
{
if (last == null )
return addToEmpty(last, data);
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
last = temp;
return last;
}
static Node addAfter(Node last, int data, int item)
{
if (last == null )
return null ;
Node temp, p;
p = last.next;
do
{
if (p.data == item)
{
temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = p.next;
p.next = temp;
if (p == last)
last = temp;
return last;
}
p = p.next;
} while (p != last.next);
Console.WriteLine(item + " not present in the list." );
return last;
}
static void traverse(Node last)
{
Node p;
if (last == null )
{
Console.WriteLine( "List is empty." );
return ;
}
p = last.next;
do
{
Console.Write(p.data + " " );
p = p.next;
}
while (p != last.next);
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node last = null ;
last = addToEmpty(last, 6);
last = addBegin(last, 4);
last = addBegin(last, 2);
last = addEnd(last, 8);
last = addEnd(last, 12);
last = addAfter(last, 10, 8);
traverse(last);
}
}
Javascript
<script>
class Node {
constructor() {
this .data = 0;
this .next = null ;
}
}
function addToEmpty(last, data) {
if (last != null ) return last;
var temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
last = temp;
last.next = last;
return last;
}
function addBegin(last, data) {
if (last == null ) return addToEmpty(last, data);
var temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
return last;
}
function addEnd(last, data) {
if (last == null ) return addToEmpty(last, data);
var temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
last = temp;
return last;
}
function addAfter(last, data, item) {
if (last == null ) return null ;
var temp, p;
p = last.next;
do {
if (p.data == item) {
temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = p.next;
p.next = temp;
if (p == last) last = temp;
return last;
}
p = p.next;
} while (p != last.next);
document.write(item + " not present in the list. <br>" );
return last;
}
function traverse(last) {
var p;
if (last == null ) {
document.write( "List is empty.<br>" );
return ;
}
p = last.next;
do {
document.write(p.data + " " );
p = p.next;
} while (p != last.next);
}
var last = null ;
last = addToEmpty(last, 6);
last = addBegin(last, 4);
last = addBegin(last, 2);
last = addEnd(last, 8);
last = addEnd(last, 12);
last = addAfter(last, 10, 8);
traverse(last);
</script>
Output:
2 4 6 8 10 12
This article is contributed by Anuj Chauhan. If you like GeeksforGeeks and would like to contribute, you can also write an article using write.geeksforgeeks.org or mail your article to review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. See your article appearing on the GeeksforGeeks main page and help other Geeks.
Please write comments if you find anything incorrect, or you want to share more information about the topic discussed above.
How To Create Circular Linked List
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/circular-singly-linked-list-insertion/
Posted by: francisviode1952.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Create Circular Linked List"
Post a Comment